The Pennsylvania National Guard is partnered with the countries of Lithuania and Côte d'Ivoire through the Department of War National Guard State Partnership Program. Pennsylvania has partnered with Lithuania since 1993 -- one of the program's original partnerships -- and announced its partnership with Cote d'Ivoire in January 2026.
The SPP evolved from a 1991 U.S. European Command decision to set up the Joint Contact Team Program in the Baltic Region with Reserve component Soldiers and Airmen.
A subsequent National Guard Bureau proposal paired U.S. states with three nations emerging from the former Soviet Bloc and the SPP was born, becoming a key U.S. security cooperation tool, facilitating cooperation across all aspects of international civil-military affairs and encouraging people-to-people ties at the state level.
This cost-effective program is administered by the National Guard Bureau, guided by State Department foreign policy goals, and executed by the state adjutants general in support of combatant commander and U.S. Chief of Mission security cooperation objectives and Department of War policy goals.
Through SPP, the National Guard conducts military-to-military engagements in support of defense security goals but also leverages whole-of-society relationships and capabilities to facilitate broader interagency and corollary engagements spanning military, government, economic and social spheres.
The SPP now includes 108 partnerships with 117 nations around the globe.
Lithuania
Since Pennsylvania's partnership with Lithuania began in 1993, the two sides have taken part in over 800 security cooperation engagements, including senior leader engagements, subject matter expert exchanges, familiarization visits and cooperative training and exercises. This includes support to the International Security Forces in Afghanistan, a National Training Center rotation in California with the Pennsylvania Army National Guard, a visit from the sitting Lithuanian President to Fort Indiantown Gap, and the first Pennsylvania governor visit to Lithuania and Poland.
A Pennsylvania National Guard member serves as the Bilateral Affairs Officer in Lithuania to coordinate security cooperation events for the PNG, multiple other service components, the geographic combatant command and the Lithuanian Armed Forces.

About Lithuania
The Republic of Lithuania, located at the geographical center of Europe, is bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east/southeast, Poland and the Kaliningrad region of Russia to the southwest, and a 43 mile coastline along the Baltic Sea to the west. Slightly larger than West Virginia, the population is approximately 3.7 million, comprised of 80 percent ethnic Lithuanian, with the remaining 20 percent split between Russian, Polish and Belarusian. The most common religious affiliations are Catholic and Lutheran.
Independent between the two World Wars, Lithuania was illegally occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940. On March 11, 1990, Lithuania became the first of the Soviet Republics to declare its independence; subsequently restructuring its economy for integration into Western European institutions. Lithuania became a full-fledged member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) on March 29, 2004, and the European Union (EU) in May 2004.
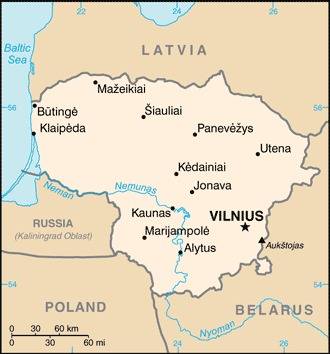
While modest amounts of recoverable oil have been discovered in the western part of the country and in adjoining areas offshore, the country remains dependent on imports for fuel and raw materials. During 2001, Lithuania continued to successfully utilize its geographic location to advance its international trade objectives.
The country has completed numerous free trade agreements which create monetary and fiscal policy as well as an improving economic situation in the country has pushed the rate of inflation down to single digit levels. Lithuania’s economic freedom score is 76.7, making its economy the 16th freest in the 2020 Index. Its overall score has increased by 2.5 points, due primarily to a higher government integrity score. Lithuania is ranked 9th among 45 countries in the Europe region, and its overall score is well above the regional and world averages.
More Information
U.S. Department of State Lithuania page
C.I.A. World Fact Book - Lithuania
Côte d’Ivoire
Pennsylvania National Guard and Côte d’Ivoire military officials announced on Jan. 13, 2026, that the Pennsylvania National Guard has been selected to partner with Côte d’Ivoire through the National Guard State Partnership Program.
Formal signing ceremonies will be conducted later in 2026 in the United States and Côte d’Ivoire.

About Côte d’Ivoire
Côte d’Ivoire, also referred to as Ivory Coast, is a West African nation with a population of about 32 million. Its political capital is Yamoussoukro, though its largest city and economic capital is the coastal city of Abidjan.
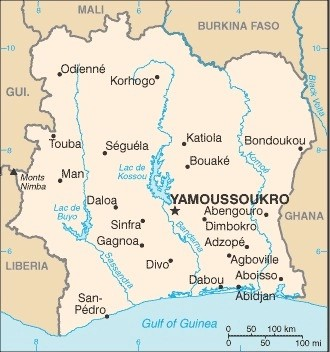
It has a strong, growing economy and is the world’s largest exporter of cocoa, which is used to make chocolate. Pennsylvania is home to several major chocolate makers, including Hershey, Mars and Godiva, and the Port of Philadelphia is the primary entry point for cocoa imported to the US.
More Information
U.S. Department of State Côte d’Ivoire page
C.I.A. World Fact Book - Côte d’Ivoire